Lunokhod 2
Lunkhod 2 was the second of two unmanned lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of the Lunokhod program. A 1970s Soviet rover did indeed travel about 3 miles farther on the surface of the moon than originally thought, meaning that any robot hoping to break its off-world distance record will have to run a full marathon, researchers say.
The remote-controlled Lunokhod 2 moon rover was long thought to have traveled 23 miles (37 kilometers) on the lunar surface back in 1973. But a Russian team recently upped the estimate to 26 miles (42 kilometers), using images snapped by NASA’s sharp-eyed Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
The primary objectives of the mission were to collect images of the lunar surface, examine ambient light levels to determine the feasibility of astronomical observations from the Moon, perform laser ranging experiments from Earth, observe solar X-rays, measure local magnetic fields, and study the soil mechanics of the lunar surface material.
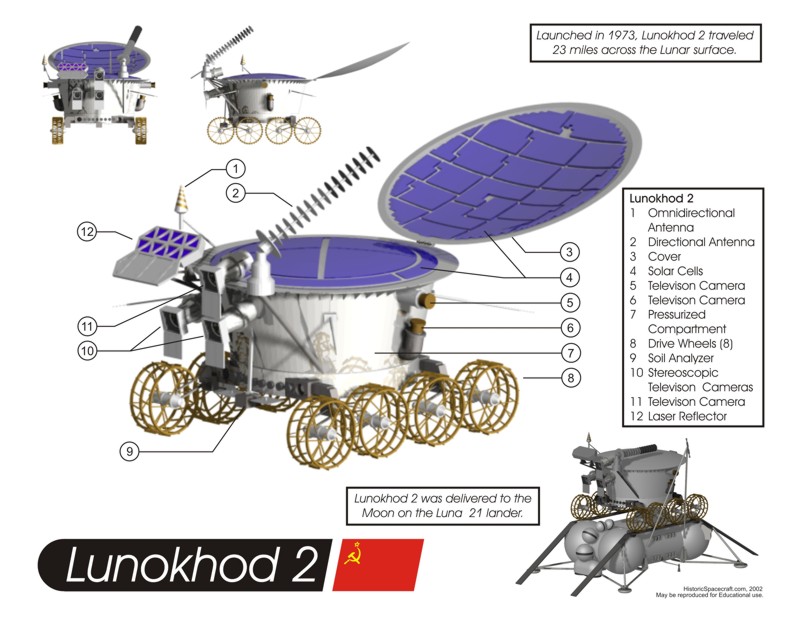
Lunokhod 2 operated for about 4 months, and the original estimate was that it covered 37 km (23 mi) of terrain, including hilly upland areas and rilles, and sent back 86 panoramic images and over 80,000 TV pictures. As of June 26, 2013, its journey remained the longest any robotic rover, or any vehicle, that had ever driven on another celestial body; the crewed Apollo 17 Lunar Roving Vehicle.
You might also like
How Have Boston Dynamics Improved Atlas Even Further?
What Is Atlas? Atlas is Boston Dynamics most attention-drawing robot to have been produced. Out of their long line of extremely impressive expressive bots, Atlas is potentially the most interesting.
Festo’s Newest Robot Is a Hopping Bionic Kangaroo
Every year, Festo comes up with innovative and fantastical new robot designsas part of its “Bionic Learning Network,” which seeks to use “principles from nature to provide inspiration for technical applications.”
Are Robot Lawyers Better Than Human Ones?
It has commonly said that robots are seemingly years away from being able to handle very human and nuanced situations that typically require an understanding of how people feel. Recently



